Grenada
Total area:
344 km2
Population:
110,000 (2000), 102,598 (2011)
Coastline:
121 km
Terrain:
Volcanic in origin with central mountains. Max elevation: 840 m
General overview
Grenada, which comprises three small islands; Grenada, Carriacou and Petit Martinique, is located approximately at 12º 07'N, 61º 40' W in the windward side of the chain of islands in the Caribbean. Grenada is the largest among these islands, with an area of around 344 km2 and an estimated population of 110,000. Its climate is tropical with an annual rainfall of 3,500 millimetres on the windward mountain sides and less than 1,500 millimetres in the lowlands. It has two seasons wet (June to November) and dry (December to May). There is highest rainfall in the wet season and this is the period of most likely occurrence of hurricanes. Grenada is volcanic in origin and its landscape is scenic with hilly landform and forested hillsides. About 77 % land area has slopes exceeding 20 degrees. Mount St. Catherine (840 meters) is the highest point on the Island. Most of the population is settled along the coastal belt and specifically in the south-west side of the main Island. Inland, there is extensive agriculture and forested area.
Basic Country Statistics and Indicators (2014)
(From http://www.preventionweb.net/countries/grd/data/)
More statistical information is available from: http://data.worldbank.org/country/grenada
|
Population |
people |
105,897 |
|---|---|---|
Urban |
% Total population |
35.583 |
Rural |
% Total population |
64.417 |
Urban population growth |
% Annual |
0.340 |
Population density |
People / km2 |
311.5 |
GDP (Gross Domestic Product) |
Million US$ |
834.074 |
GDP per capita |
Million US$ |
7,890.513 |
Capital stock |
Million US$ |
4,536 |
GFCF (Gross Fixed Capital Formation) |
Million US$ |
144.579 |
Social Expenditure |
Million US$ |
74 |
Gross Savings |
Million US$ |
-68.345 |
Total reserves |
Million US$ |
150.571 |
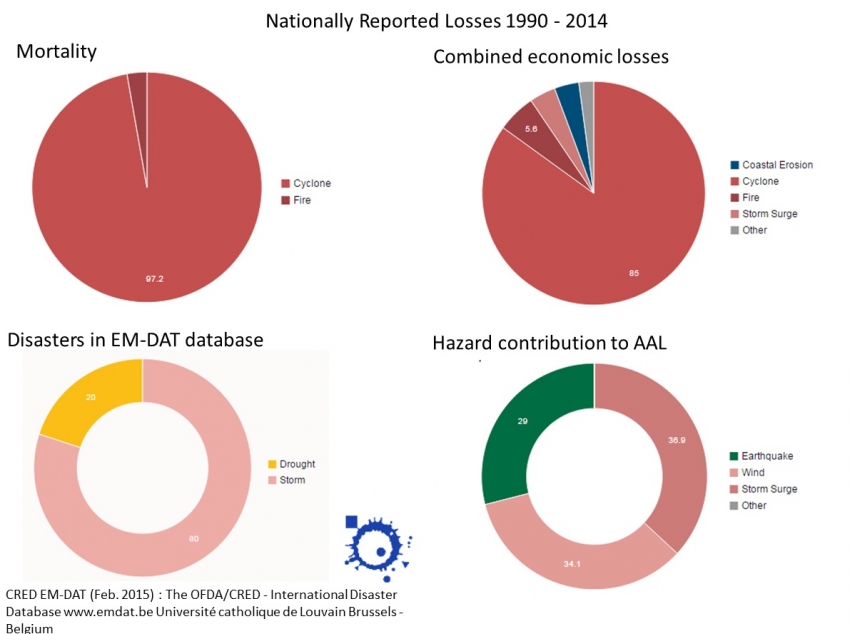
Nationally Reported Losses 1990 - 2014
(From http://www.preventionweb.net/countries/grd/data/)
|
8-year moving average 2005-2013 |
Extensive [%] |
Intensive [%] |
|
|---|---|---|---|
DataCards |
3.38 |
100.00 |
0.00 |
Deaths |
0.00 |
100.00 |
0.00 |
House destroyed |
1.25 |
100.00 |
0.00 |
House damaged |
724.88 |
100.00 |
0.00 |
Injured people |
0.13 |
100.00 |
0.00 |
Displaced people |
923.75 |
50.00 |
0.00 |
Combined economic loss (US$) |
8,420,840.50 |
100.00 |
0.00 |
Probabilistic risk results, Average Annual Loss (AAL) by hazard
(From http://www.preventionweb.net/countries/grd/data/)
|
Hazard |
Absolute |
Capital |
GFCF |
Social |
Total |
Gross |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Earthquake |
8.60 |
0.190 |
5.948 |
11.653 |
5.712 |
-12.583 |
Wind |
10.12 |
0.223 |
7.000 |
13.712 |
6.721 |
-14.807 |
Storm Surge |
10.95 |
0.241 |
7.574 |
14.837 |
7.272 |
-16.022 |
Tsunami |
0.01 |
0.000 |
0.007 |
0.014 |
0.007 |
-0.015 |
Multi-Hazard |
29.68 |
0.654 |
20.529 |
40.215 |
19.712 |
-43.427 |
Natural hazards:
Historically, Grenada was considered relatively safe from hurricanes owing to its location in the southernmost region of the hurricane belt, with 3 hurricanes since the beginning of the 20th century. However, the country was heavily affected by Hurricane Ivan in 2004, and Hurricane Emily in 2005. There are two active volcanoes in Grenada, Mount St. Catherine in the center of the island and the submarine volcano Kick-€˜em-Jenny located 8 km north of the island, which has lead to tsunami in the past. Flood risk in grenada is largely associated with storm surge in low lying coastal areas. Flash flooding from mountain streams coupled with storm surge events are the primary causes of flood events and effects are generally limited to communities located in the coastal margins along stream passages. landslides are a common event in Grenada, with much of the impact experienced along the roadway network.
Download World Bank GFDRR report on Grenada
Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2015




